Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions
In Chapter 6 the classical potential theory of the random walk is covered in the spirit of 16 and 10 and a. While the emphasis of this text is on simulation and approximate techniques understanding the theory and being able to find exact distributions is important for further study in probability and statistics.

Continuous Probability Distribution An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Special cases Mode at a bound.
. PX 0 PTT 1 4 PX 1 PHT. Conditional probabilities allow us to account for information we have about our system of interest. For example we might expect the probability that it will rain tomorrow in general to be smaller than the probability it will rain tomorrow given that it is cloudy todayThis latter probability is a conditional probability since it accounts for relevant.
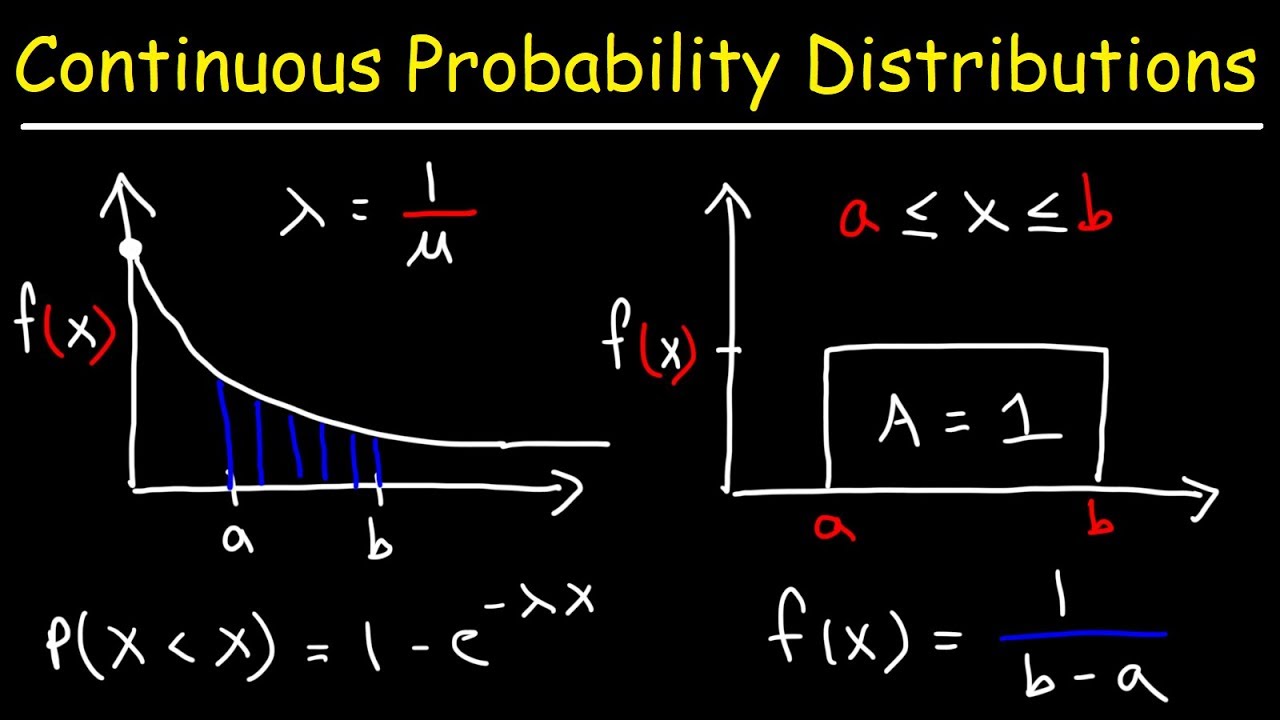
2 Continuous Probability Densities 41. With rate parameter 1. Schaums Outline of Probability and Statistics CHAPTER 2 Random Variables and Probability Distributions 35 EXAMPLE 22 Find the probability function corresponding to the random variable X of Example 21.
12 Continuous-time random walk 12 13 Other lattices 14 14 Other walks 16. Is done by using Fourier analysis to express the probability of interest 6. Preface 7 in terms of an integral and then estimating the integral.
Order statistics sampled from an exponential distribution. For random samples from an exponential distribution with parameter λ the order statistics X i for i 123 n each have distribution where the Z j are iid standard exponential random variables ie. Where which is the actual distribution of the difference.
In this chapter we discuss the theory necessary to find the distribution of a transformation of one or more random variables. Let Y be the random variable which represents the toss of a coin. DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS to mean that the probability is 23 that a roll of a die will have a value which does not exceed 4.
Assuming that the coin is fair we have Then The probability function is thus given by Table 2-2. Chapter 14 Transformations of Random Variables. This distribution for a 0 b 1 and c 0 is the distribution of X X 1 X 2 where X 1 X 2 are two independent random variables with standard.
The distribution simplifies when c a or c bFor example if a 0 b 1 and c 1 then the PDF and CDF become. Distribution of the absolute difference of two standard uniform variables.

Stat 2040 Chapter 6 Continuous Random Variables And Continuous Probabil Oneclass
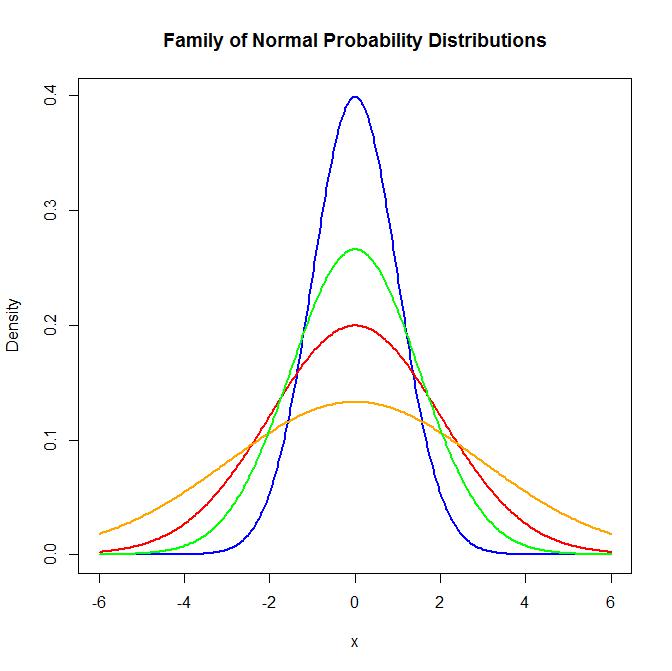
Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website
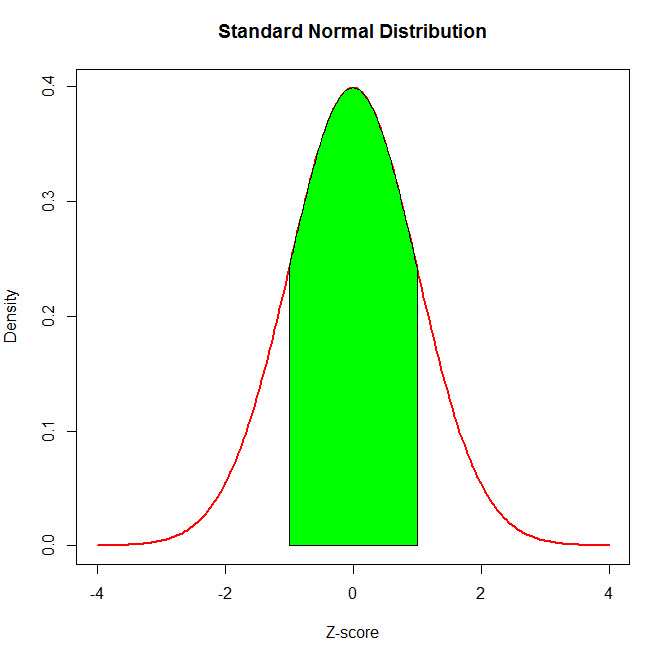
Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website

An Introduction To Continuous Probability Distributions Youtube
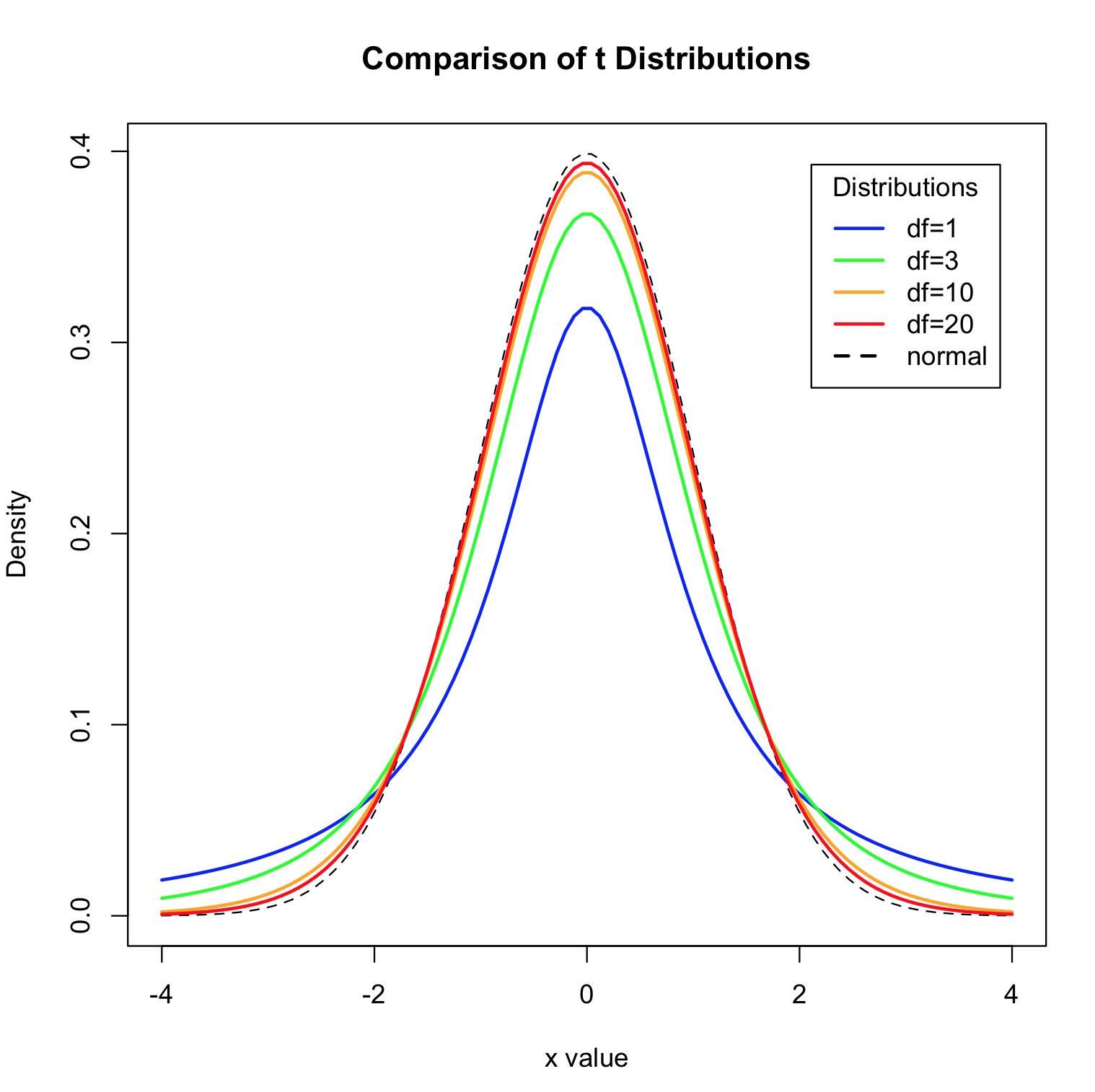
Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website

Continuous Probability Distributions Basic Introduction Youtube
0 Response to "Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions"
Post a Comment